In the specific application of water treatment, selecting the appropriate filter is a crucial step to ensure water quality meets the standards. Quartz sand filters and activated carbon filters are two widely used water treatment devices that address different water quality issues through different filtration principles. Although these two types of filters may appear similar in appearance, their working principles, structural design, and application scenarios each have their own characteristics. This article will delve into the filtration principles, equipment structure, maintenance requirements, and applicable scenarios of these two types of water treatment filters to help users make more accurate choices in practical applications.
Filtration principles are at the core of determining the performance of a filter. Different types of filters use different principles to remove impurities from water. The following is a detailed explanation of the filtration principles of quartz sand filters and activated carbon filters.
The quartz sand filter uses quartz sand as the main filter medium, removing suspended solids, particles, and impurities from water through physical interception. As water flows through the layer of quartz sand, larger particles are intercepted on the surface or within the sand layer, while smaller particles are captured by the gaps between the sand grains. The high specific surface area and low filtration resistance of quartz sand make this type of filter perform well in removing suspended solids.
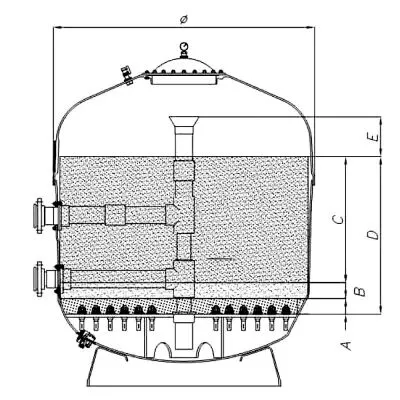
Working Principle: The activated carbon filter removes organic matter, odors, color, and other pollutants from water through the chemical adsorption effect of activated carbon. Activated carbon contains a large number of micropores, which have an extremely high specific surface area and strong adsorption capacity. When water passes through the activated carbon bed, organic pollutants, colloids, and heavy metals are adsorbed on the surface and pores of the activated carbon, thereby purifying the water quality.
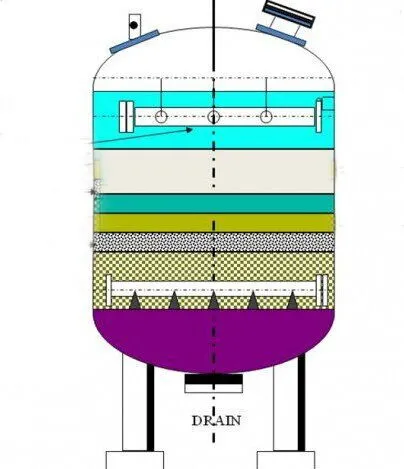
Quartz sand filters and activated carbon filters each have their unique characteristics, and their advantages reflect their distinct filtration principles and application areas. Understanding these advantages can help make the most suitable choice for practical applications. Here are the main advantages of each type of filter.
Low Filtration Resistance: The large specific surface area of quartz sand effectively reduces water flow resistance.
Acid and Alkali Resistance: It has strong acid and alkali resistance, suitable for various water quality conditions.
Pollution Resistance: Not easily contaminated, suitable for treating various industrial, domestic, and wastewater.
Strong Adsorption Capacity: The microporous structure of activated carbon effectively adsorbs organic matter and odors in water.
Removal of Heavy Metals: Capable of removing heavy metal ions and other harmful substances from water.
Reduction of COD Value: Effectively reduces the chemical oxygen demand (COD) in water, improving water quality.
In the water treatment system, there are significant differences in the equipment structure and maintenance requirements of quartz sand filters and activated carbon filters. Understanding these differences helps to effectively manage and use these devices to ensure their efficient operation and long-term stability.
The structure of a quartz sand filter is usually relatively simple, mainly including a filtration container filled with quartz sand, inlets and outlets, and a backwash system. It is designed to support high-flux treatment tasks and can withstand relatively high working pressures.
Regular Backwashing: To maintain good filtration effects, it is necessary to regularly backwash the quartz sand to remove accumulated impurities.
Filter Medium Replacement: Quartz sand has a long service life, but it needs to be replaced when worn or severely contaminated.
The activated carbon filter is filled with a coarse quartz sand cushion layer and high-quality activated carbon. The equipment is more complex, requiring the even distribution of activated carbon and good water flow channels.
Activated Carbon Replacement: The adsorption capacity of activated carbon decreases with use, so it needs to be replaced regularly.
Cleaning: Regularly inspect and clean the equipment to ensure its normal operation and efficient filtration.
Quartz sand filters and activated carbon filters each have unique filtration principles and characteristics, making them suitable for different application scenarios. The following are the main application scenarios of these two types of filters in their respective fields.
Power and Electronics Industry: Used for treating circulating water and process water.
Food and Beverage Industry: Removes suspended solids and particles from water.
Municipal Engineering: Used for urban water supply and wastewater treatment.
Swimming Pools: Removes impurities and suspended solids from pool water.
Applicable Situations: Suitable for treating large-volume water bodies, especially effective in removing large particle impurities and suspended solids.
Drinking Water Treatment: Removes odors, organic matter, and heavy metals from water.
Food Processing: Removes harmful substances and odors from water.
Wastewater Treatment: Used for in-depth treatment of municipal and industrial wastewater.
Aquariums: Removes harmful substances from water to protect the health of aquatic life.
Applicable Situations: Suitable for occasions that require in-depth water quality treatment, odor and organic pollutant removal, especially outstanding in high-requirement water quality improvement tasks.
In summary, quartz sand filters and activated carbon filters play different roles in the field of water treatment. Quartz sand filters effectively remove suspended solids and particles from water through physical interception and are suitable for various industrial water and municipal water treatment applications. Activated carbon filters, on the other hand, remove organic matter, odors, and heavy metals from water through chemical adsorption, making them particularly suitable for occasions that require a high level of water quality improvement. Understanding the working principles, structural characteristics, and maintenance requirements of these two types of filters will help in selecting the most appropriate equipment in actual operations, ensuring the efficiency and stability of the water treatment system.

 English
English Español
Español русский
русский