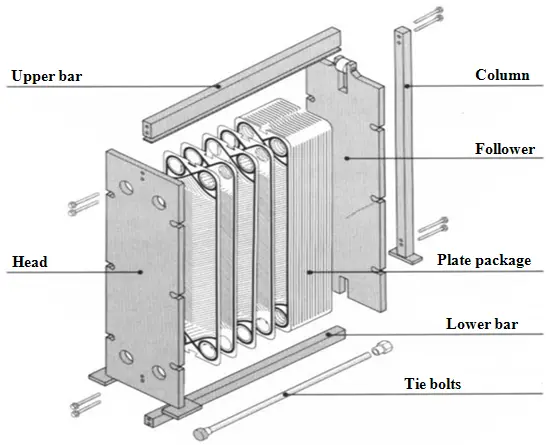
In the continuous evolution of refrigeration technology, heat exchangers play a pivotal role as essential components of refrigeration equipment. In recent years, plate heat exchangers have been increasingly adopted in refrigeration technology, showcasing strong potential for development. Compared to traditional shell-and-tube heat exchangers commonly used in refrigeration, refrigeration-specific plate heat exchangers not only possess the general characteristics of plate heat exchangers but also offer unique advantages.
1. Reduced Refrigerant Usage
Traditional shell-and-tube heat exchangers require substantial amounts of refrigerants to maintain the proper functioning of refrigeration systems due to their large shell-side and tube-side volumes. However, this practice not only escalates costs but also poses environmental pollution risks. Conversely, plate heat exchangers, with their smaller size and narrower spacing, significantly reduce the volume of refrigerant required, thus promoting environmental preservation and lowering operational costs. This advantage positions plate heat exchangers as an environmentally friendly and energy-efficient solution in refrigeration technology.
2. Enhanced Freeze Resistance
The turbulent flow of water in plate heat exchangers at low velocities ensures a more uniform temperature distribution. This characteristic greatly diminishes the tendency of freezing in the system. Even in the event of freezing, plate heat exchangers exhibit better resilience against the pressures generated by freezing compared to shell-and-tube counterparts, minimizing the risk of tube rupture due to thermal expansion. Moreover, plate heat exchangers can resume operation after thawing, ensuring uninterrupted performance in refrigeration systems.
3. Improved Evaporation Efficiency
In plate heat exchangers, refrigerants evaporate more readily, achieving complete evaporation and transitioning to a liquid-free state more efficiently. Consequently, refrigeration systems often do not require separate gas-liquid separators, simplifying system configurations and enhancing evaporation efficiency. Additionally, the modular design of plate heat exchangers facilitates straightforward installation, maintenance, and transportation, further reducing operational costs. This increased cost-effectiveness makes plate heat exchangers a viable solution for widespread adoption in refrigeration applications.
In summary, the application of advanced fully-welded plate heat exchangers in refrigeration technology not only meets the requirements for reducing equipment weight, volume, and metal consumption but also offers significant benefits such as environmental sustainability, enhanced freeze resistance, and improved cost-effectiveness. The promising prospects and developmental potential of these innovations present new opportunities and challenges for the refrigeration industry.

 English
English Español
Español русский
русский