Different types of heat exchange equipment are compared from the following aspects: high efficiency, compact structure, material saving, low pressure drop, reliable structure, low manufacturing cost, easy installation, maintenance, and long service life.
2. How to describe the model of heat exchanger?
DN is the nominal diameter of the heat exchanger, which is the inner diameter of the rolled cylinder and the outer diameter of the steel cylinder. A is the nominal heat exchange area of the heat exchanger, based on the outer diameter of the heat exchange tube. LN is the nominal length, which refers to the length of the heat exchange tube. S is the heat exchange tube (only for aluminum, copper, titanium). Pt/ps is the design pressure of the tube/shell side. ClassⅠ tube bundle refers to the use of higher-level cold-drawn heat exchange tubes, suitable for occasions without phase change heat transfer and easy to produce vibration. ClassⅡtube bundles are ordinary cold drawn heat exchange tubes, which are suitable for general occasions such as reboiling, condensation heat transfer and no vibration. ClassⅠandⅡ tube bundles are limited to carbon steel and low alloy steel. The representation method is as follows:
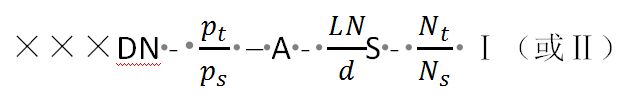
3. What are the standards of selecting heat exchanger?
For a certain heat load, the selection of heat exchanger should consider the following points:
(1) Material of heat exchanger
(2) Change of operating pressure and temperature
(3) Quantity of flow
(4) Type of flow
(5) Performance parameters - thermal efficiency and pressure drop
(6) Fouling tendency
(7) Fluid types and phase states
(8) Possibility of maintenance, inspection, cleaning, expansion and repair
(9) Overall economy
(10) Manufacturing technology
(11) Other uses
4. How to select heat exchange equipment?
The selection of heat exchange equipment should keep to the following principles:
(1) It is wise to choose the shell-and-tube heat exchanger as the reliability of strength is very important operated at high temperature and high pressure when handling capacity is large.
(2) For highly corrosive fluids, the heat exchanger with corrosion-resistant material shall be selected.
(3) If the operating pressure and temperature are not high and the processing capacity is not large, but the fluid has corrosive requirements to use precious metal materials, you can choose the new heat exchanger of the plate type heat exchanger (plate type, plate fin type are those kind of heat exchangers with high heat transfer efficiency, compact structure and less metal consumption).

 English
English Español
Español русский
русский